How To Explain Mitosis To Children
After fertilization, the cell of the newly formed embryo must originate all the others until a complete organism is created. Once formed, it must grow, and during this process, the cells in your body mature, multiply, and die. But how do cells reproduce? In this article we will see how to explain the process of cellular reproduction, mitosis, to children.
What is mitosis ?: explanation for children
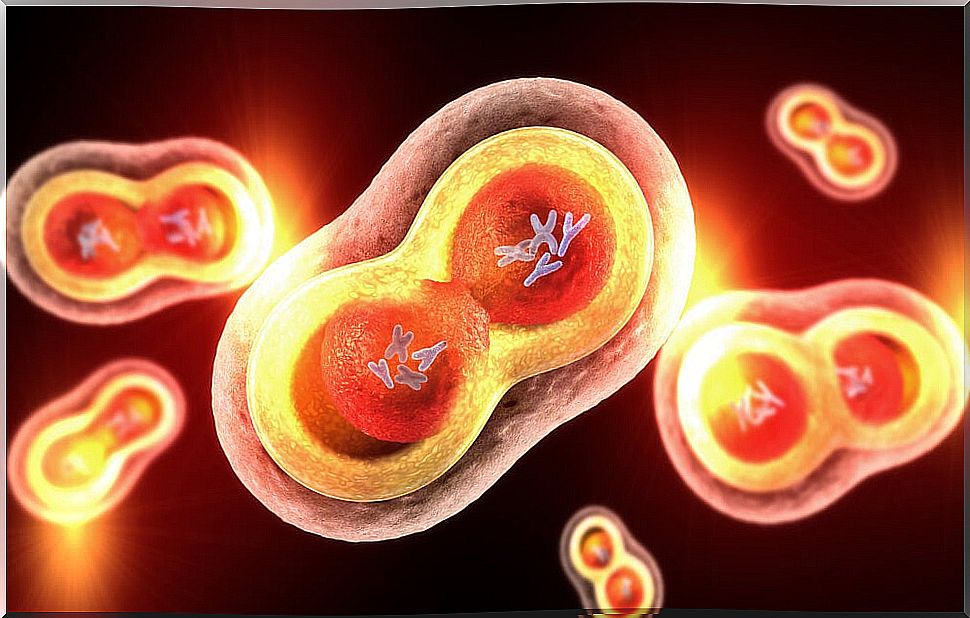
Mitosis is the process by which cells multiply. It is one of the 2 stages that make up the cell cycle and takes place after the duplication of genetic material. As a result, two daughter cells equal to the mother cell are obtained.
Mitosis takes place in somatic cells, or what is the same, any cell of the body that is not a gamete. Gametes are formed by another process called meiosis, which is not cell multiplication, but quite the opposite, division.
The cells of our body resort to mitosis when we need to grow or repair a wound caused in a tissue, a bone, an organ. How does the mitosis process develop?
Phases of mitosis explained for children
For cells to reproduce, a previous phase is necessary, the Interface, during which the genetic material is duplicated, the cell goes from having 23 pairs of chromosomes to 46 pairs. In addition, some organelles, such as centrioles, duplicate, while others disappear and then, in a matter of hours, are synthesized again.
In this way, everything is ready for the cell to enter mitosis. The process takes place in 4 clearly differentiated phases: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase.
Phase 1: Prophase
- The genetic material of the cells begins to condense and the chromosomes are visualized.
- The nuclear membrane becomes destabilized and disappears.
- The centrioles, one of the most important organelles for this process, duplicate and begin to travel towards the cell poles.
phase 2: the metaphase
To better understand this phase we must imagine the cell as a sphere similar to the Earth.
- At the poles we will have the centrioles located, from which fibers that resemble the latitude lines of the Earth will begin to grow. This structure is called the mitotic spindle.
- The chromosomes directed by the fibers of this spindle go to the equator of the cells, staying there aligned forming the equatorial plate.
phase 3: the anaphase
Once the chromosomes are aligned, the centrioles begin to pick up the fibers from the mitotic spindle. This causes the chromosomes trapped in the fibers, and shaped like an 8-armed spider, to split in two and be dragged towards the poles. Now, each chromosome once again has two chromatic, or what is the same, 4 arms.
Phase 4: Telophase
Once the chromosomes have positioned themselves at opposite poles of the cell, they begin to decondense. At the same time, the cell will again form the nuclear membrane around them from the aster fibers of the centrioles.
Final stage of the mitosis process explained for children: cytokinesis
At this point, it only remains to physically divide the mother cell to originate the two daughter cells. Paradoxically, the process of cell multiplication, in the end, is a division, so that the mother cell disappears converted into two daughter cells.
The resulting daughter cells will be genetically the same as the mother and will contain the same organelles as the mother. Although the function they develop will depend on the genes that are expressed and the degree of maturation of the original cell.
What happens if mistakes are made during mitosis?
The errors that can occur during the process are very few, since the cell has a strict quality system and stops the production process if the error is fatal. This fact does not mean that errors can occur, especially in the first zygote divisions. If this error cannot be repaired and the cell cycle continues its course, the abnormality may turn out to be undetectable to carcinogenic.
One of the most frequent errors is the nondisjunction of the chromosomes , where one of the homologous chromosomes does not separate correctly during anaphase. As a result, we obtain a daughter cell with three chromosomes, trisomy , and the other with only one, aneuploidy .
At other times, chromosomes can be damaged, either by breaking one of their arms, causing a deletion, or a fragment can be incorporated into a chromosome of another pair, causing a translocation. It may also be the case that the fragment integrates in the reverse direction on the same chromosome, causing an inversion.
And to finish…
To finish this article on how to explain mitosis to children, a curiosity. The process was first described in 1848 by the German botanist Wilhelm Hofmeister, who was studying the embryonic development of higher plants. However, Walther Flemming is credited with the discovery, as he was the first to see chromosomes in division.